Prerequisite: Graph Concepts
A Minimum Spanning Tree (MST) is the cheapest set of edges that connect graph vertices together. For instance, servers on a network or destinations on a road map. Stated differently, an MST is the sub-set of edges with the minimum possible sum of edge weights. A MST must satisfy two properties.
- Does not contain a cycle
- A path exists between every pair of vertices
Based on the definition of a MST, the following facts logically apply:
- All connected graphs have at least one MST
- There are often multiple valid MSTs for a given graph
- An MST has $n-1$ edges.
The image below is a graphical representation of an input graph and its MST.
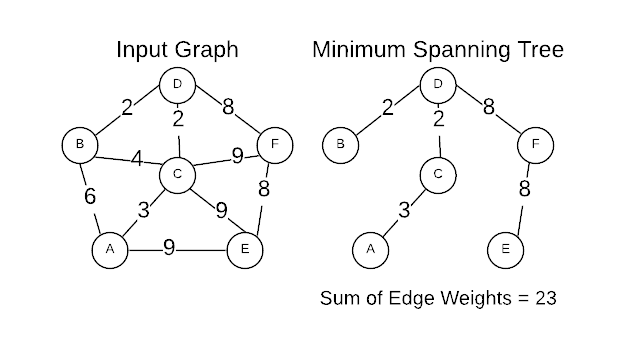
This section explore algorithms for efficiently identifying the minimum spanning tree for a given graph.
Applications
- Find the minimal connected sub-routes of a network (e.g. electrical grid, computer network) that will make it fully connected for the minimum cost
- Defining a taxonomy
- With a slight modification, Kruskal’s algorithm can be used for single-link clustering.
Source Code
Relevant Directories:
Click here for build and run instructions